


 |
| Fig: Fangs in different snake families |
Table: Difference between poisonous and non-poisonous snakes
| ||
Features
|
Venomous/poisonous snakes
|
Non-venomous/non-poisonous snakes
|
Physical features
|
Stout, dull color
|
Slender, brightly colored
|
Saliva
|
Contains toxic peptides and enzymes
|
Non-toxic
|
Tail
|
Compressed
|
Rounded
|
Ventral (belly) scales
|
Broad and always extends across the entire width of the belly
|
Small/ moderately large, never extends across the belly
|
Vertebral (back) scales
|
Enlarged as in Krait
|
Not so
|
Head scales
|
Usually smaller. It could be larger also and when larger, will possess special features such as:
|
Usually larger and without any special features
|
• A pit between eye and nose as in pit viper
| ||
• A third supra-labial scale touching the eye and nasal shield, as in cobra, king cobra
| ||
• A large fourth Infralabial shield, as in krait
| ||
Teeth
|
Upper jaw has a pair of teeth modified into fangs that are grooved (Cobra) or channelised (viper)
|
All teeth are uniform and small in size and there are no fangs.
|
Usually there are 4 longitudinal rows of teeth in upper jaw and 2 rows in lower jaw.
| ||
Bite marks
|
Usually two (fang marks)
|
More than two
|
Nocturnal habit
|
Usually nocturnal
|
Not nocturnal
|
 |
| Figure- A to H: Important features of poisonous and non-poisonous snakes: (A) Poison apparatus and fangs (canalised and grooved), (B) Ventral shields (belly scales) and vertebrals, (C) Head scales, (D) Cobra (note the hood and spectacle mark) (E) Cobra – Third supralabial touching eye and nasal shield, (F) Krait — four infralabials (note the large fourth one), (G) Krait — enlarged vertebrals on the back, and (H) Pit viper — a pit between eye and nostril. |
Table: Non-poisonous snakes resembling poisonous snake
| ||||
Non-poisonous snake
|
Poisonous snake
| |||
Rat snake
|
Common cobra
| |||
Common cat snake
|
Saw-scaled viper
| |||
Banded kukri
|
Banded krait
| |||
Sand boa
|
Russell’s viper
| |||
Common wolf snake
|
Common krait
| |||
 |
| Fig: Common cobra |
 |
| Fig: Dorsal aspect of cobra with marks |
 |
| Fig: Common krait |
 |
| Fig: Common krait head |
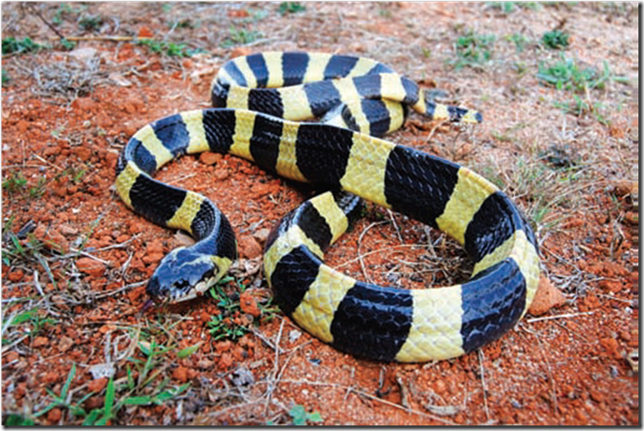 |
| Fig: Banded krait |
 |
| Fig: Saw scaled viper |
 |
| Fig: Russell’s viper |
Fatal dose and amount of venom injected per bite
| ||||
Cobra
|
12 mg of dried venom
|
200—350 mg
| ||
Krait
|
6 mg of dried venom
|
20—22 mg
| ||
Russell’s viper
|
15 mg of dried venom
|
150—200 mg
| ||
Saw scaled viper
|
8 mg of dried venom
|
25 mg
| ||
 |
| Fig: Bite area in elapid bite |
 |
| Fig: Flow chart showing clinical features in elapid bite |
 |
| Fig: Local features in Viperid bite |
 |
| Fig: Local features in Viperid bite |

 |
| Fig: First aid in snakebite |
